Risk Management


Challenges and Opportunities
In an era of rapid change—driven by environmental, technological, regulatory, and economic challenges—effective risk and crisis management is crucial to ensuring stable and sustainable growth.
Ratch Pathana Group adopts a proactive risk management approach by systematically analyzing and assessing potential risks that could impact our operations. We have also developed a comprehensive Business Continuity Plan (BCP) to address crises and ensure that our business can adapt and continue operating under all circumstances. Through robust and effective risk management, we are committed to strengthening our business resilience, enhancing competitiveness, and creating long-term value for all stakeholders.
Management Approach and Value Creation
Risk Management
Recognizing the importance of risk management, the company conducts continuous assessment, analysis, and monitoring of various risk factors to identify both business opportunities and potential threats to the energy sector. Key risks include geopolitical risks, which contribute to ongoing volatility and rising energy prices. Simultaneously, evolving energy policies are increasingly shifting toward renewable energy adoption to combat climate change. Moreover, advancements in energy production technologies, particularly in solar energy, wind energy, and energy storage solutions are reshaping the energy sector's infrastructure. Increased investments in clean energy present both opportunities and challenges for businesses. Strategic direction with energy market trends while proactively managing both opportunities and risks arising from rapid industry changes.
The company implements an enterprise-wide risk management and mitigation of potential impacts, while maintaining the company’s competitive capabilities in a highly uncertain and volatile business environment, the company has adopted the 2017 COSO Enterprise Risk Management (COSO ERM) framework internationally recognized as a foundation for defining its risk framework and guiding adaptive strategies in alignment with energy market trends. This approach enables the company to manage rapidly changing business opportunities and risks, emphasizing enterprise-wide risk management within an established Risk Appetite. The framework encompasses strategic, financial, operational, and compliance risk management, as well as environmental, social, and governance (ESG) risks, ensuring alignment with the organization’s objectives and goals.
The group conducts regular risk management reviews, reporting and presenting performance results to the Governance and Risk Management Committee for monitoring, oversight, and policy recommendations. These results are also presented to the Board of Directors to evaluate the effectiveness of risk management and governance processes across the organization. This approach ensures a comprehensive, holistic, and effective risk management process that supports sustainable business objectives.
Sustainability Risk Management

The Corporate Governance and Risk Management Committee recognizes the importance of managing the constantly evolving economic, social, and environmental landscape. As a result, the committee conducts assessments and analyzes the risks and opportunities arising from sustainability issues that may impact the organization, including its subsidiaries and projects, both from internal and external factors. Additionally, the committee reviews risk management plans by applying the organization’s overall risk management framework to address risks related to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) aspects as follows:
| Goals | Performance |
|---|---|
| 1. Zero claims of non-compliance | Number of claims of non-compliance 0 claims |
| 2. Zero incidents of non-compliance | Number of incidents of non-compliance 0 incidents |
| 3. Zero ESG issues | Number of ESG issues 0 issues |
| 4. Zero fines and settlements specified for ESG issues in audited accounts | Provisions for fines and settlements specified for ESG issues 0 baht |
Economic and Governance Risks
Risk Factors and Opportunities
The economic landscape, along with fluctuations in oil prices, may impact on the pricing of electricity and steam. These fluctuations could, in turn, affect the overall demand for energy, the cost of key raw materials, and foreign exchange rates. Additionally, shifts in government policies may influence the strategic direction of business development.
Risk Management
- Strategic Business and Investment Planning Aligned with a Dynamic Economic Landscape.
- Analyze risk factors that may impact the organization’s objectives.
- Develop contingency plans to address potential changes and uncertainties.
- Continuously monitor operational performance to ensure alignment with strategic goals.
Risk Factors and Opportunities
The rapid evolution of innovation and technology in the energy sector presents both opportunities and risks for businesses. If organizations fail to adapt or invest appropriately in new technologies, they may experience a loss of competitive edge. Additionally, reliance on outdated technologies or legacy systems can reduce operational efficiency, thereby impacting the financial stability of the business.
Risk Management
- Study innovative approaches in the energy business and assess the risks associated with investments in new technologies and innovations, including an analysis of expected returns.
- Continuously monitor information, news, and evaluate the evolving landscape of new technologies.
Risk Factors and Opportunities
IT systems are the part that can support business operations for convenient, fast, competitive, and can create business differences. The evolution of cyber threats is becoming more sophisticated and intense. It is therefore a channel for cyber attacks on the company's collective database. Loss of sensitive or financial information Affecting the confidence and performance of the company. Therefore, it is a challenge to reduce the impact. The company has set the key risk management measures as follows:
- It is scheduled to replace IT equipment every 3-5 years. The replacement model must have better performance, including a security system, intrusion prevention system and backup.
- Install advanced systems and programs to protect data security from cyber threats such as Deep Discovery Inspector, WAF, Hyper Converged Infrastructure (HCI), Dell VXRail Server, Data Leak Prevention (DLP), Cyber Command Intelligent Threat Detection and Response (as disclosed in the Annual Registration Statement (Form 56-1 One Report) Topic “Risk Management”.
Risk Management
- A policy for maintaining cybersecurity and information technology security is in place, with the establishment of task forces in each area to ensure preparedness. Training is provided to employees to raise awareness of the policy and the Cybersecurity Act B.E. 2562 (2019).
- Communications and public awareness campaigns about the legal aspects and recommendations for using information technology are carried out through screen notifications when using computers or the intranet. This ensures that all employees are informed and aware of the importance of the Cybersecurity Act B.E. 2562 (2019).
Risk Factors and Opportunities
The improper use and disclosure of personal data, if not handled with adequate precautions, could lead to significant losses and impact current business operations. It is essential to comply with legal regulations and any amendments to laws related to data protection.
Risk Management
- The company complies with the Personal Data Protection Act and relevant laws to ensure strict protection of personal data. Regular monitoring and audits are conducted to ensure compliance with the laws.
- The company has a Data Protection Policy in place to safeguard personal data.
- The company has implemented programs to obtain consent (both through forms and verbal agreements) in accordance with the Personal Data Protection Act B.E. 2562 (2019).
Social Risk
Risk Factors and Opportunities
The company has assessed human rights risks to prevent and mitigate the impact of such risks. The assessment of human rights risks related to labor includes the following aspects: employee working conditions, employee health and safety, discrimination and harassment against employees, freedom of association, assembly, and collective bargaining, and the use of illegal labor. Based on the risk assessment results, the company ensures compliance with labor practices and human rights standards. The company has a fair and standardized employee selection system, including written tests and interviews, to evaluate knowledge, skills, and the suitability of individuals for specific job positions. The company adheres to principles of fairness and equality in human rights in accordance with its human rights policies and practices, ensuring no discrimination based on gender, religion, political rights, or any other factors. Furthermore, the company provides internal employees with the opportunity to apply for vacant positions if their qualifications are suitable. If no suitable internal candidates are found, the company will then proceed with external recruitment.
Risk Management
- Compliance with Human Rights Policies and Practices:
- - The company does not engage in or support any activities that violate human rights.
- - The company upholds the principles of independence and respects diversity in thought, gender, race, religion, politics, and other matters. It ensures that expressions or opinions that could lead to conflict or division are avoided.
- - The company provides channels for communication with employees, allowing those who feel they have been treated unfairly to submit complaints. These complaints will be addressed with attention and fairness.
- - The company requires that all employees and contractors be at least 20 years of age, and it prohibits the employment of child labor or the use of forced labor, as well as any form of gender discrimination.
- Training and providing information to all new employees before they start work, as well as conducting training for contractors before commencing work to ensure they understand safety, environmental, and energy-related issues, along with the company's goals, policies, regulations, and compliance requirements.
- Establishing a welfare committee within the organization to involve employees in determining the criteria, benefits, and welfare programs that go beyond the legal requirements, demonstrating a commitment to employee care and well-being.
- Continuously monitoring information, news, and evaluating the situation.
Risk Factors and Opportunities
The company’s operations may involve accidents or emergencies that could impact on the safety of employees and workers, as well as affect the confidence of local communities and society.
Risk Management
- Manage safety, occupational health, and environmental operations through an environmental management system (ISO 14001) and an occupational health and safety management system (ISO 45001). Regularly review hazard identification and risk assessment processes to ensure the safety and well-being of employees and contractors working within the company.
- Develop manuals and conduct drills for emergency and disaster preparedness, such as fire and chemical spill scenarios.
- Implement safety awareness programs to enhance the safety consciousness of employees and contractors working in the organization.
Risk Factors and Opportunities
Following the global outbreak of COVID-19, changes in biological factors, the environment, and human behavior, along with extreme climate change, may lead to the spread of severe infectious diseases or emerging diseases. These outbreaks can have a severe impact on public health, posing challenges to both health and economic systems. The operations of employees and workers, as well as business continuity, are significantly affected. Additionally, the outbreak of emerging diseases is characterized by unpredictability and constantly evolving patterns, making it difficult to forecast with accuracy.
Risk Management
- Developed a Business Continuity Plan (BCP) to mitigate potential impacts on the company from disruptive events.
- Implemented measures to prevent the spread of infections, aiming to reduce severe health risks for employees and on-site workers.
- Provided training to employees to raise awareness of emerging infectious diseases and severe communicable diseases, with an emphasis on preventing and minimizing the risk of infections both at the workplace and in nearby communities.
- Continuously monitored news and updates, assessed risks, and closely monitored events.
Risk Factors and Opportunities
The energy business, especially electricity generation, is of interest to society, so there is a risk of being rejected or not being accepted in the business. If there is an impact on safety, occupational health, environment to the community and society acceptance and trust from the community and society. It is an important factor that affects long-term business development.
Risk Management
- Establish guidelines and develop plans to prevent and reduce safety, occupational health, and environmental impacts, as well as to improve the quality of life for employees and nearby communities.
- Set up a department responsible for enhancing the organization's image by following the company’s sustainability policy, monitoring performance, and carrying out community relations activities in the area to foster ongoing communication and understanding with the community.
- Foster community engagement by listening to feedback from the community, creating a communication manual, and implementing a process for handling community complaints.
Environmental Risks
Risk Factors and Opportunities
Climate change and natural disasters resulting from global warming are becoming increasingly severe, leading to various risks. These risks include direct impacts, such as natural disasters and droughts, and indirect impacts, such as stricter regulations, new standards, changes in consumer behavior, and technological transformations. The Ratch Pathana Group recognizes the importance of addressing these issues and is actively working to reduce greenhouse gas emissions in a tangible way. This effort aligns with global initiatives to tackle the climate crisis as an urgent priority. The company is committed to focusing on the development and investment in renewable energy businesses.
Risk Management
- Establish policies to address climate change and appoint a working committee for greenhouse gas management to drive the organization's greenhouse gas reduction efforts.
- Set greenhouse gas management targets aimed at achieving Carbon Neutrality by 2050, and report greenhouse gas management performance to the Sustainability Committee and the Board of Directors accordingly.
- Assess the organization’s greenhouse gas emissions and removals by registering the organization's Carbon Footprint (CFO) and Product Carbon Footprint (CFP) with the Thailand Greenhouse Gas Management Organization (Public Organization) or TGO.
- Continuously monitor information, news, and evaluate situations to assess organizational risks.
- Communicate the importance of, and encourage participation in, greenhouse gas reduction measures to all employees and stakeholders to address climate change.
Risk Factors and Opportunities
The company strictly adheres to laws and regulations related to environmental impacts and safety. A designated department is responsible for monitoring and analyzing results, ensuring compliance with the evolving legal and regulatory landscape. This includes continuous tracking of changes in laws and regulations that may affect environmental impact and safety. This proactive approach allows the company to develop timely measures and contingency plans to mitigate potential environmental risks.
Risk Management
- Environmental Management: Managed through an Environmental Management System (ISO 14001).
- Policy Implementation: Adhered to policies related to quality, environment, safety, and energy conservation.
- Environmental, Safety, and Occupational Health Handbook: Developed a manual to guide operations and monitor performance in environmental management, safety, and occupational health.
- Emergency Response Plan: Prepared emergency response plans, created operational manuals, conducted training sessions, and performed drills to test equipment and alarm systems in accordance with the defined schedule, ensuring strict adherence to the guidelines.
- Impact Mitigation and Environmental Monitoring: Reported the results of monitoring mitigation measures and environmental quality checks to the Office of Natural Resources and Environmental Policy and Planning, the Energy Regulatory Commission, the Department of Industrial Works, the Industrial Office, local administrative organizations, and relevant agencies.
Emerging Risk Management
Emerging risks are new, previously unforeseen risks that carry a high degree of uncertainty. Both the likelihood of occurrence and the potential impacts are often difficult to assess clearly, as these risks may arise in the future and affect the company’s operations over the next 3-5 years. It is imperative for the company to prioritize and consider the impacts of rapid changes in economic, environmental, social, cultural, and technological conditions. These changes can present both challenges and opportunities for business development. Examples include technological advancements, government policies related to energy development, innovations in adapting to and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The following are emerging risks that may affect the company's business operations:
Artificial Intelligence is rapidly developing and could have significant implications for the energy sector. The integration of AI in power plant operations offers opportunities to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and assist in predictive problem-solving, as well as enhancing management and operational processes. For instance, AI could be used to monitor and control automation systems within power plants, such as analyzing data from sensors and control systems to predict machinery failures or wear-and-tear (predictive maintenance). This could reduce downtime and enhance production efficiency. However, uncertainties may arise if the AI system makes decisions based on incorrect or incomplete data, leading to erroneous decisions, which could result in system malfunctions or disruptions in power plant operations. Additionally, there is a cybersecurity risk related to the connectivity of network systems.
Furthermore, the use of AI may lead to labor shifts, reducing the need for certain job roles, but at the same time, it presents opportunities for training and developing new skills. Therefore, the consideration of AI application requires careful investment planning and risk management to ensure long-term benefits.
Risk Management
- Monitor technological changes that support and align with operations and power generation.
- Study and evaluate AI technologies that can be utilized to improve efficiency and reduce operational costs.
- Educate employees to prepare for the integration of AI in enhancing the organization’s capabilities.
The development of energy production technologies and innovations presents the company with opportunities to enhance production efficiency or leverage them for business expansion. However, innovations that are still in the early stages of development may involve uncertainties related to technology, performance, safety, and economic viability.
Additionally, the Energy Transition Risk—stemming from the shift from fossil fuels to green energy—poses a new challenge for the power plant business across all dimensions, including increased costs, intensified competition, and regulatory uncertainties. Nevertheless, if the company can adapt by investing in clean energy, incorporating technologies to improve efficiency, and strategically implementing ESG practices, power plant businesses can survive and achieve sustainable growth in the future.
New Risk Factors That May Significantly Impact the Energy Business and Preventive Measures:
- Energy Production Technology Innovations: Continuously monitor technological advancements and explore the feasibility of integrating new innovations into operations. This includes overseeing production control and maintenance of power plants, as well as solar energy projects.
- Renewable Energy Technology and Competition Affecting Costs (e.g., Solar and Wind Energy): Monitor the prices of materials and equipment that may impact projects, and review the results of feasibility studies for new projects, as rapidly decreasing costs for solar and wind energy technologies could affect profitability and project viability.
- Advanced Energy Storage Technologies: Investigate developments in technology to enhance the efficiency and stability of energy production and continuous power delivery systems.
- Energy Transition Risks Leading to Potential Stranded Assets: The transition to cleaner energy could render fossil-fuel-based power plants at risk of becoming stranded assets if they must shut down before the end of their useful life. Continuously manage operations and monitor changes in government policies, regulations, and power development plans.
- Need for Skilled Personnel in Clean Energy Innovations: Develop and implement plans to recruit and train human resources that align with the business’s clean energy objectives, ensuring a workforce capable of meeting future industry demands.
- Fuel Energy and the Promotion of Renewable Energy Projects: Support the shift towards renewable energy, including solar, wind, and biomass, by advancing and investing in these technologies, in line with the company’s commitment to clean energy and sustainability.
Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
The company places great emphasis on the development and management of business continuity to ensure the uninterrupted operation of the business during abnormal situations, whether caused by external or internal threats such as pandemics, cyberattacks, natural disasters, civil unrest, protests, etc. Each threat has the potential to cause harm to lives and property, as well as create obstacles to business operations. An effective and systematic approach to Business Continuity Management (BCM) enables the organization to quickly restore operations. The Corporate Governance and Risk Management Committee has outlined procedures to prepare for crisis situations, ensuring that the Ratchaburi Group's management systems are capable of responding to challenges and addressing operational inefficiencies effectively and continuously. The creation of the Business Continuity Plan (BCP) ensures that it can be effectively implemented when needed.
Ratch Pathana Energy Public Company Limited and its subsidiaries recognize the importance of Business Continuity Management (BCM) to ensure that, in the event of a crisis or emergency, the organization can restore operations swiftly with minimal disruption. This approach safeguards the interests of stakeholders and ensures long-term business sustainability.
Objectives
- To provide a framework for managing business continuity, ensuring the protection and safety of employees' lives and the organization's assets, as well as maintaining customer service.
- To prepare for emergencies or disasters by developing and implementing preventive and crisis management plans.
- To establish a process for managing responses and restoring operations to normal within an appropriate timeframe.
- To reduce the severity of the impacts caused by business disruptions and minimize significant losses to an acceptable level.
Business Continuity Management Approach
- Implement a business continuity management system based on recognized industry standards, with continuous improvements and development.
- Establish a working group responsible for managing the business continuity plan, overseeing and supporting the overall continuity efforts across the organization.
- Promote and support all levels of leadership and employees in developing awareness and understanding of business continuity management, as well as enhancing and building personnel competencies in preparing measures to ensure ongoing operations. This will lead to effective implementation.
- Ensure that all leaders and employees at every level participate in adhering to the business continuity management policy and take actions to help the organization achieve its business continuity goals. Focus on regularly reviewing and updating the business continuity management plan, conducting drills, and cultivating a corporate culture centered around business continuity.
Examples of ESG Incidents and Responses
| ESG Incidents | Response Plans | |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental | Fire |
|
| Flood |
|
|
| Drought |
|
|
| Social | Pandemic |
|
| Governance | Human rights violation |
|
Crisis Management and Business Continuity Management (BCM) Integration into Corporate Culture. The company has emphasized the importance of Business Continuity Management (BCM) as part of its corporate culture, ensuring that employees at all levels understand its significance. Every individual is aware of their roles and responsibilities in maintaining business operations during times of crisis. The Ratch Pathana Group has consistently developed and conducted annual Business Continuity Plan (BCP) drills, with the 2024 drill achieving an excellent evaluation score of 90%.
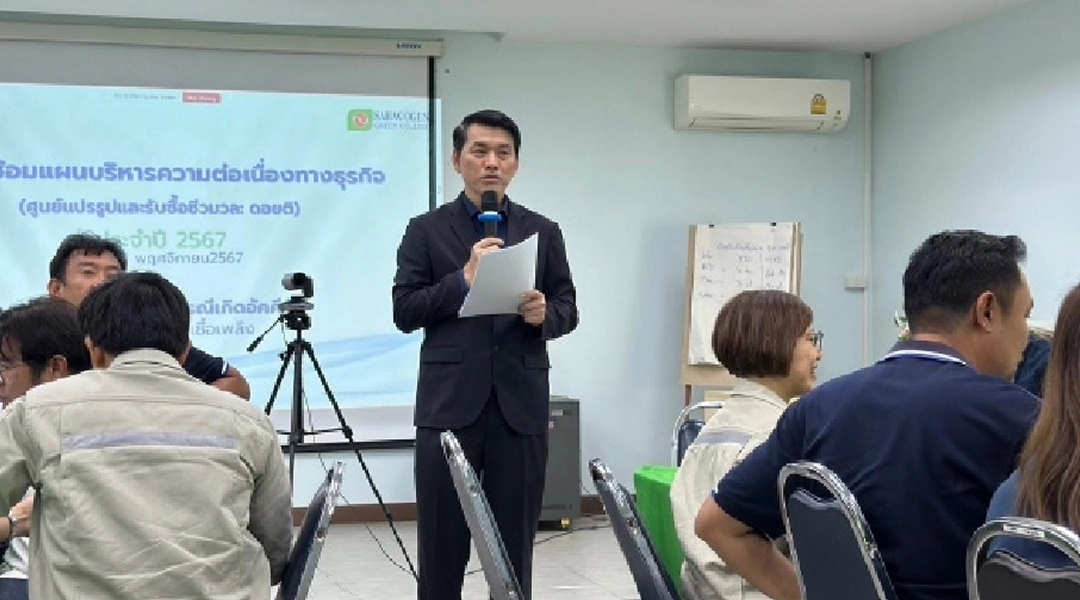

In 2024, subsidiaries such as Sahacogen Green Co., Ltd. and Sahagreen Forest Co., Ltd. conducted training courses on "Techniques for Developing and Practicing Business Continuity Plans (BCP)." The objective was to enhance understanding of BCM principles and ensure the accurate and effective application of BCP strategies. A total of 40 executives and employees participated in and successfully completed the training.
Standards for Managing Sustainability Risks
The company places great importance on managing sustainability risks by using international standards as a guide to its business operations, aiming to achieve a balance between economic, social, and environmental growth. This balance is the foundation for sustainable organizational development. The company adopts the practices of the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) as a framework for disclosing sustainability information, with a focus on systematic risk management that encompasses all aspects of the business. This includes managing potential impacts on stakeholders by integrating organizational risk management with risks related to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, using the COSO ERM Framework. Furthermore, the company adheres to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs), which consist of 17 main goals, as a guide to define the organization’s strategies and policies.
Managing sustainability risks is a critical factor for businesses to consider in an era where climate change and the demand for sustainable energy are receiving increasing global attention. Operating a power plant with responsibility toward the environment and society not only responds to stakeholder expectations but also strengthens long-term financial stability. Therefore, the company integrates internationally recognized standards and guidelines, including the GRI Standards and the UN SDGs, into the sustainability risk management of its power plant operations.


The implementation of GRI Standards enables the company to assess and manage risks related to energy production that may have an environmental impact, such as emissions, waste management, and biodiversity preservation. From a social perspective, power plant businesses should consider respecting labor rights, community engagement, and complying with social regulations that may affect the business. Managing social risks according to GRI standards helps power plants establish positive and sustainable relationships with surrounding communities, while also ensuring responsibility for the safety and health of employees and local populations. In terms of governance, GRI Standards facilitate transparent disclosure of information related to sustainability operations and potential risks arising from internal management practices. Although the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are not directly a risk management standard, using SDGs as a strategic framework helps power plant businesses gain a deeper understanding of sustainable development and enables more effective management of sustainability-related risks.






